As the summer months are fast approaching, it is always best to have an emergency kit on hand in case of rolling blackouts. Perishable foods can be at risk if a power outage occurs and can easily cause food-borne illnesses (1). As we know, those most vulnerable to food poisoning are the young and elderly population (2). Therefore, it is essential to try and be prepared before the summer months arrive.
Here are some tips on preparing an emergency kit and what you will need to do in case of a power outage.
The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) suggests (3):
Stock up on non-perishable foods-at least several days’ worth. This includes food such as:
- Ready-to-eat canned foods
- Canned foods packed with protein-such as canned tuna, chicken, turkey, low-sodium soups, and chili
- Canned vegetables- such as carrots, corn, peas, or green beans
- Protein or fruit bars
- Spread protein-packed foods throughout the day to maintain adequate nutrition (4)
- Dry goods such as powdered eggs, multigrain cereals, or granola
- It is important to have enough fiber to increase fullness and energy maintenance (5)
- Peanut butter or nut butter alternative
- Dried fruits- such as raisins, apricots, cranberries, or dried plums
- Canned Juices-such as V8 vegetable juices
- Shelf-stable pasteurized milk or milk alternatives
- High energy foods
- Comfort/stress foods
- Water- enough to keep well hydrated.
- The suggested amount is one gallon per person per day (6)
For our participants, we recommend that you have a minimum of five shelf-stable meals prepped and ready to go in an emergency. We provide these emergency meal kits to all congregate and home delivered meal participants twice per year. These meal kits help maintain senior nutrition and provide easy access to food during emergencies.
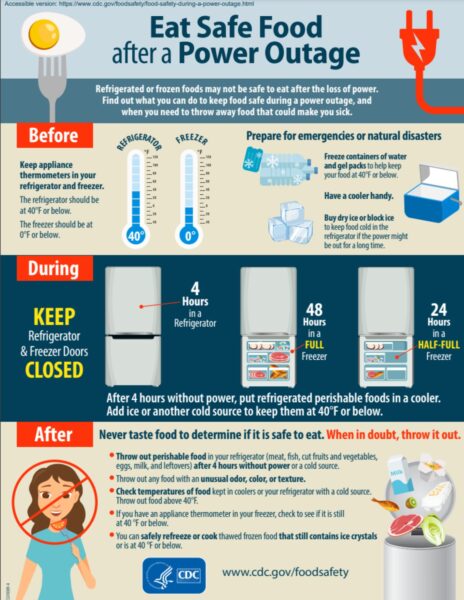
How to Manage Food without Power
- Keep the refrigerator and freezer doors closed as much as possible.
- The fridge/freezer should keep foods cold for about 4 hours if unopened.
- If power is out for less than 4 hours, the food should be safe (3).
- Discard any cold foods such as meat, poultry,
fish, eggs, or leftovers that have been above 40
degrees Fahrenheit for two or more hours. - If canned foods look swollen, dented, or visibly
damaged it’s best to be on the safe side and
not consume them (3). - Throw away foods that have developed an
obvious odor, color, or texture change.
References: 1.https://www.cdc.gov/foodsafety/food-safety-during-a-power-outage.html
2.https://www.fda.gov/food/consumers/people-risk-foodborne-illness 3.
https://www.ready.gov/food#power 4.Deer, R. R., & Volpi, E. (2015). Protein intake and muscle function in older adults. Current opinion in clinical nutrition and metabolic care, 18(3), 248–253. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCO.0000000000000162
5.https://acl.gov/sites/default/files/nutrition/Nutrition-Needs_Fiber_FINAL-2.19-FINAL_508.pdf
6.https://www.fema.gov/txt/library/f&web.txt#:~:text=Store%20at%20least%20one%20gallon,each
%20member%20of%20your%20family 7.https://www.cdc.gov/foodsafety/food-safety-during-apower-
outage.html